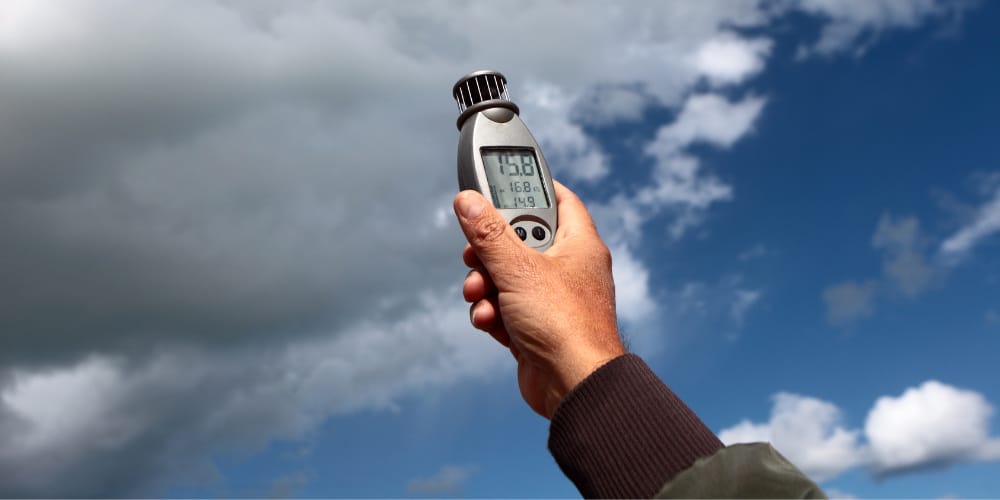
Measuring wind has always been a human need, from guiding sailors at sea to protecting modern cities during storms. Anemometers make this possible by providing accurate data on wind speed and direction, information that communities and industries depend on each day. Farmers, engineers, pilots, and even local weather stations rely on these instruments to make informed decisions that affect safety and productivity. A closer look at how anemometers work, the different types available, and their wide range of uses helps us appreciate their role in daily life. This article shares everything you need to know in simple, clear terms.
What Is an Anemometer?
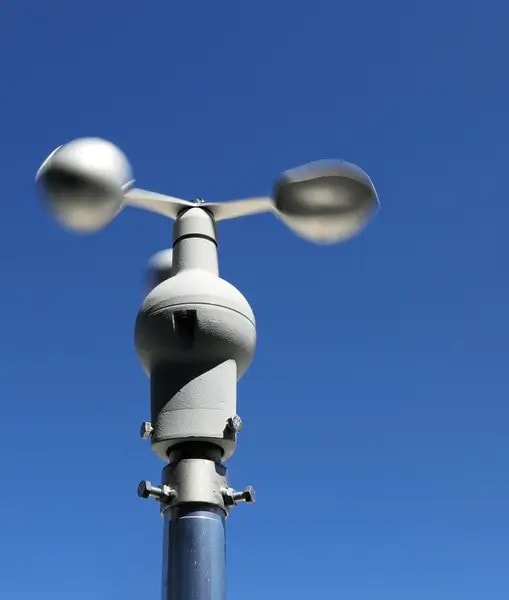
An anemometer is a device that measures wind speed and direction, and it has become an important tool in weather forecasting, aviation, and construction safety. The science behind measuring wind explains how it captures air movement through spinning cups, vanes, or digital sensors that translate wind force into precise readings. Farmers rely on it to plan irrigation and spraying, while engineers use it to monitor crane operations and site conditions. Its accuracy helps protect lives, equipment, and projects that depend on reliable wind data.
Main Types of Anemometers
Different industries rely on anemometers for accurate wind readings, and over the years, several designs have been created to meet diverse needs. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses; understanding these differences helps people choose the right tool for their work.
Cup Anemometers
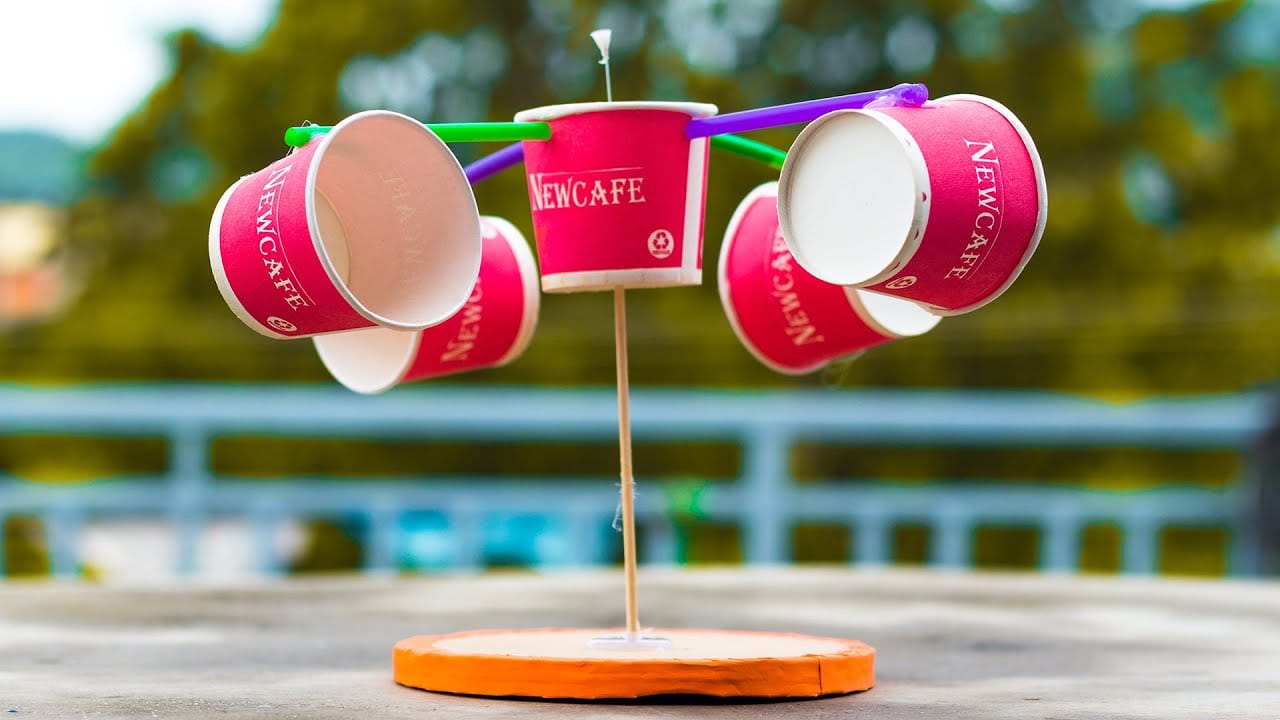
Cup anemometers use small cups that spin as wind passes through them. Their design is simple and has been used for decades in weather stations.
Pros: They are reliable, easy to use, and can give consistent readings in different conditions.
Cons: They have moving parts that wear out over time and may give less accurate readings in very light or gusty winds.
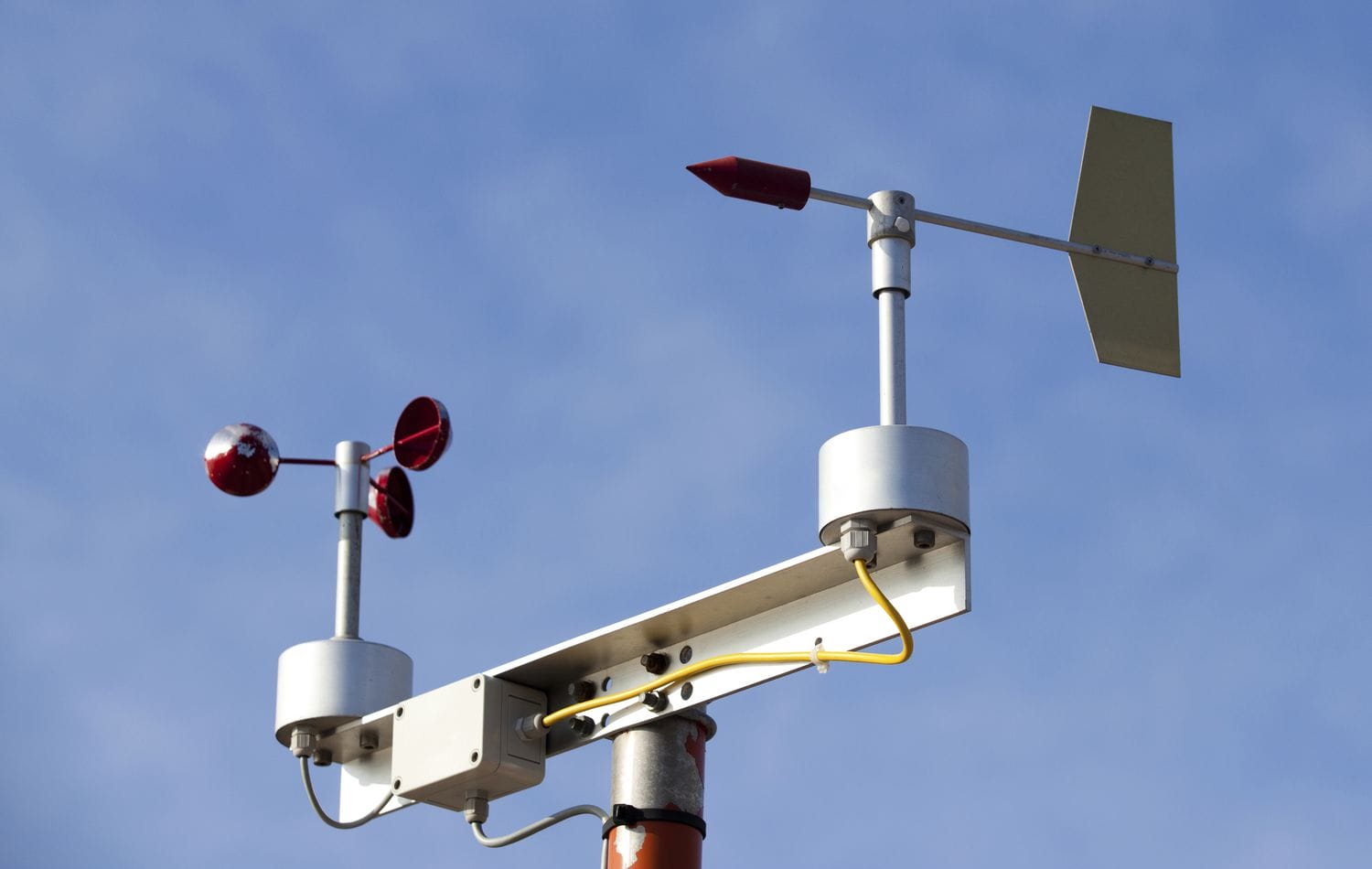
Vane or Propeller Anemometers
This type combines a propeller with a vane that helps it face the wind. It is widely used in environmental studies and site monitoring.
Pros: It gives both wind speed and direction at the same time. The design is straightforward and easy to understand.
Cons: The device can struggle in turbulent air and requires regular checking to stay accurate.
Hot-Wire Anemometers
Hot-wire anemometers measure wind speed using a heated wire that cools down when air flows across it. The change in temperature is used to calculate speed.
Pros: They can detect very small changes in air movement and are useful in laboratories.
Cons: They are fragile, expensive, and not well suited for outdoor use in tough conditions.
Ultrasonic Anemometers
These anemometers use sound waves to measure wind without any moving parts.
Pros: They are highly accurate, work well in all directions, and require little maintenance.
Cons: The cost is higher than other types, and performance may be affected by rain or ice.
Pressure Tube (Pitot Tube)
Pitot tubes calculate wind speed by measuring pressure differences as air flows through them.
Pros: They are durable and effective for high-speed measurements, especially in aviation.
Cons: They are less sensitive at low speeds and can be affected by dirt or blockages.
Features to Consider When Choosing One
Selecting the right anemometer is a decision that requires thought, since the tool will influence how reliable your weather readings turn out. A good choice makes the difference between accurate monitoring and guesswork, especially in industries where wind affects safety and productivity. While the options may look similar, their features can vary in ways that matter a lot for real-world use.
Accuracy Range
Accuracy should be the first thing to think about, because the purpose of an anemometer is to measure wind correctly. A small error in readings can affect construction timelines, aviation schedules, or even farming activities. The accuracy range gives you confidence that the numbers you see are dependable, and this saves time and resources.
Wind Speed and Direction Capabilities
Another important feature is the ability to capture both wind speed and direction. Some models only provide speed, but direction can be just as important. For instance, crane operators need both pieces of information to make safe decisions on lifting heavy loads. A device that tracks both allows for better planning and avoids risks.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Anemometers face harsh outdoor conditions, which is why durability and weather resistance should be checked carefully. Rain, dust, and direct sun can shorten the life of a weaker model. Choosing one that has a strong build and can withstand exposure means you will use it reliably for many seasons without constant replacements.
Mounting Type
The way an anemometer is mounted affects its performance. Some are designed for handheld use, while others need to be fixed on poles, cranes, or rooftops. Picking the right mounting type depends on where and how often you plan to use it.
Digital vs. Analog Output
The choice between digital and analog output depends on your needs. Digital devices give clear, easy-to-read displays, while analog models are simpler and often preferred in places where technology support may be limited.
Smart Features
Modern anemometers now come with smart features such as wireless data transfer or mobile connectivity. These allow users to track wind information from a distance, making the process more convenient and timely.
Where and How They’re Used
Anemometers uses span in many areas of work and daily life because they make invisible air movement measurable. Their readings help people make sound decisions, improve safety, and support planning. Understanding where these instruments are installed also shows how much different sectors depend on reliable wind data.
Common Job Site Installations
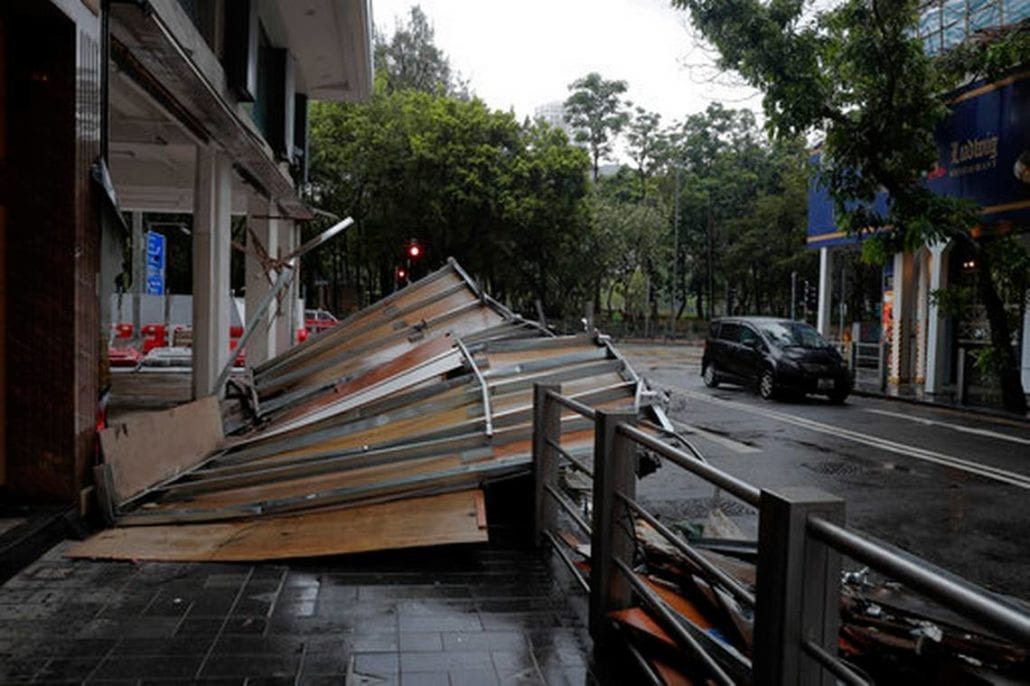
Construction projects often use anemometers to protect workers and equipment. Tall cranes, scaffolding, and temporary roofing can all become dangerous if winds rise unexpectedly. Contractors place wind meters on cranes and high platforms so operators can check real-time conditions before lifting heavy materials. This simple precaution reduces accidents and gives workers confidence as they go about their tasks.
Use in Weather Stations and Airports
Weather stations rely on accurate wind speed and direction to prepare forecasts that communities trust. Airports depend heavily on these devices since aircraft safety is closely tied to changing wind conditions. Pilots receive detailed updates from air traffic controllers, allowing them to make safe landings and takeoffs. Passengers may not notice, but their smooth travel depends on the small instrument spinning in the wind.
Marine Environments
Ships at sea face powerful winds and shifting currents, making anemometers indispensable on bridges and decks. Mariners depend on them for navigation, sailing adjustments, and storm preparation. Fishing crews, ferry operators, and shipping companies all gain an added layer of safety through these continuous readings.
Industrial Safety Systems
Factories, warehouses, and chemical plants use wind sensors to track airflow and prevent hazards. Proper ventilation removes fumes and keeps indoor conditions safe for employees. In outdoor industrial yards, monitoring wind reduces the chance of accidents when storing lightweight materials or handling dust.
Wind Energy Sites
Wind farms cannot operate without precise wind measurements. Anemometers help determine the best turbine placement, monitor day-to-day performance, and guide maintenance schedules. Reliable data means power companies can generate electricity safely and efficiently while protecting their investments in clean energy.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and regular maintenance make a big difference in how well an anemometer performs. A small effort at the start helps keep readings accurate and reliable over time, while steady care keeps the device working smoothly.
Best Practices for Positioning
An anemometer should always be placed in an open area where wind flows freely. A rooftop or mast often works well, provided it is higher than nearby buildings and trees.
Avoiding Obstruction and Interference
Anything that blocks or redirects airflow can reduce accuracy. Always check that no walls, poles, or heavy cables sit close to the device.
Calibration Frequency
Regular calibration maintains confidence in readings. Most devices benefit from being checked at least once or twice a year, depending on usage.
Cleaning and Battery Checks
Dust, insects, and moisture can interfere with sensors. Gentle cleaning and timely battery replacement keep the device dependable.
Who Uses Anemometers and Why It Matters
Understanding who relies on anemometers helps show why these devices play such a meaningful role in both daily life and professional work. Wind affects safety, planning, and decision making, and the right equipment gives people the confidence to act on reliable data.
Professionals Who Use Anemometers
Anemometers are not just for scientists. Different professionals depend on them, each for specific reasons:
- Crane operators use them to judge safe lifting conditions.
- Farmers track wind to protect crops and manage spraying.
- Pilots and airport staff rely on wind readings for safe flights.
- Mariners and fishermen use them to read weather conditions at sea.
- Construction crews monitor wind for safety on high-rise projects.
- Event organizers check the wind to protect outdoor stages and tents.
Industry Needs and Device Types
Every industry requires a device that fits its working environment. Portable handheld models help workers who need quick checks in the field. Fixed wireless units are better suited for construction sites or cranes where continuous monitoring is needed. More advanced stations combine wind speed with data on temperature or humidity, giving a broader picture for those who need more than a single reading.
Why Accuracy Matters
Small errors in wind readings can lead to unsafe decisions. A pilot who misjudges crosswinds or a crane operator who lifts during sudden gusts puts people and equipment at risk. Accurate anemometers help professionals act with confidence, protect investments, and keep teams safe.
Conclusion
Wind never stops moving, and your equipment should never stop delivering reliable data. WirelessWind provides wireless wind solutions that keep you informed in real time. Contact us today and let us help you choose the right system for your safety and success.













